Our latest research provides a summary of key developments since June 2024 on national 5G security initiatives in the 27 EU member states, Norway, Switzerland, and the UK.
Germany and Estonia were added to the list of countries that banned Huawei and/or ZTE. Based on publicly available information, these countries, together with Romania and Sweden, are the only EU countries that explicitly banned Chinese 5G equipment vendors.
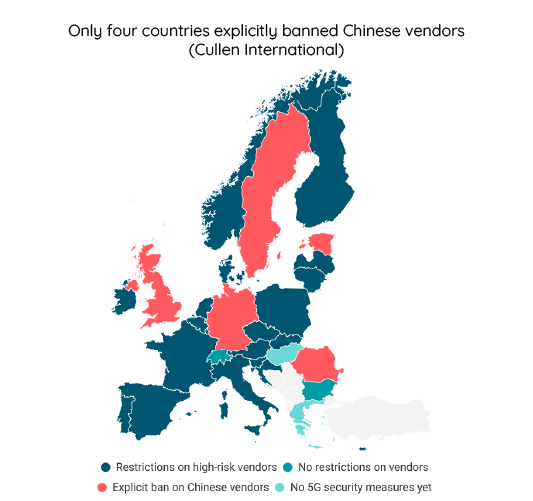
Estonia
Elisa contested the decision of Estonian administrative authorities that labelled Huawei as an HRV before the administrative court of Tallinn. The court requested a preliminary ruling from the Court of Justice of the EU (CJEU).
The CJEU will address several questions, for example whether:
- the Estonian legislation restricting HRVs is compatible with EU law, including the principle of proportionality; and
- the requirement to remove already deployed hardware and software could be considered as expropriation of property.
Germany
The German government announced in July 2024 that mobile network operators (MNOs) should stop using 5G critical components from Huawei and ZTE by the end of 2026 in the core network.
In the RAN, MNOs can still use antennas from the above vendors, but they will replace network management systems (NMS) with solutions from other vendors by the end of 2029.
The restrictions would be laid down in contracts concluded between the government and MNOs.
For more information and access to our full benchmark on 5G security measures across Europe, please click on “Access the full content” - or on “Request Access”, in case you are not subscribed to our European Digital Economy service.
>> See also our benchmark on 5G security measures across the Americas!
more news
04 February 25
Indexation of retail prices in European telecoms contracts
Cullen International’s benchmark on indexation of retail prices looks at the rules allowing operators in 15 European countries to increase prices based on indexation clauses included in their contracts.
29 January 25
Brazil applies tougher rules for IoT than other countries in the Americas
Our latest research analyzes the key regulatory issues for the provision of cross-border IoT connectivity in the Americas.
27 January 25
SingPost results improve on the back of e-commerce and international revenues
An overview of Singapore’s postal sector: our new report covers the Singapore regulatory framework, including the USO, licensing regime, price regulation, letter boxes, parcel lockers, and competition.