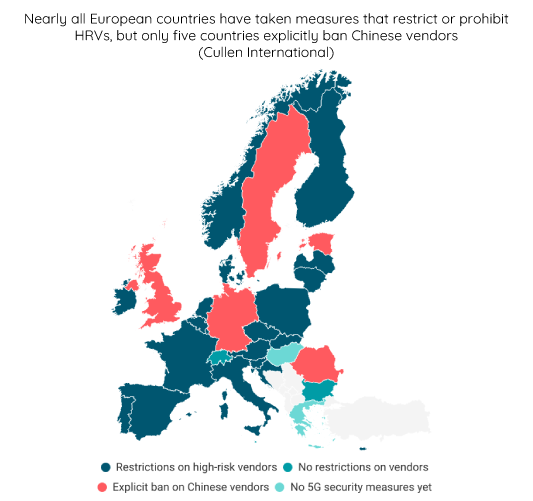
Our latest research provides a summary of key developments since January 2025 on national 5G security initiatives in the 27 EU member states, Norway, Switzerland, and the UK.
Relevant developments have been observed in Norway, Poland and Sweden.
In Norway, the new Electronic Communications Act entered into force on 1 January 2025. It enables national authorities to refuse the granting of spectrum frequency licences to equipment vendors from countries without a security agreement with Norway. This was also possible within the previous framework, but the legal basis is made more explicit in the new legislation.
In Poland, the latest amendments to the draft Cybersecurity Act were presented on 7 February 2025. The amendments would maintain the proposed obligation for telecoms operators to withdraw equipment from high-risk vendors (HRVs) within four years after their designation.
The European Commission filed an application to intervene as a non-disputing party in the arbitration proceeding initiated by Huawei against Sweden before the World Bank Group’s International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). The Commission aimed to address the EU rules on the security of 5G networks and member states’ margin of discretion in defining and ensuring their essential security interests. On 26 June 2024, the ICSID allowed this. The final outcome of the case is pending.
For more information and access to our full benchmark on 5G security measures across Europe, please click on “Access the full content” - or on “Request Access”, in case you are not subscribed to our European Digital Economy service.
more news
02 April 25
Common approaches to the protection of sensitive data and the personal data of minors across the Americas
Our new benchmark addresses how sensitive personal data is defined in eight countries in the Americas. It also lists what special protection measures apply to sensitive personal data and the personal data of minors.
31 March 25
APAC countries apply diverse regulatory rules to global IoT providers
Our new research compares the approach to regulation for IoT and M2M (machine-to-machine) connectivity in Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, New Zealand, and Singapore.
27 March 25
Many MENA countries taking steps to switch off 2G and 3G networks
Our latest benchmark on 2G and 3G networks switch-off shows the status in 13 MENA countries.